WHAT BURNS MORE FAT…WALKING OR HIIT?
Everyone has wondered at some point in time which form of exercise is better to burn fat; low intensity or high intensity? Steady State or HIIT? To put it in simple terms, both low and high intensity exercises will help you to burn off body fat. The question here should be… which is the most EFFECTIVE way to burn off MORE body fat?
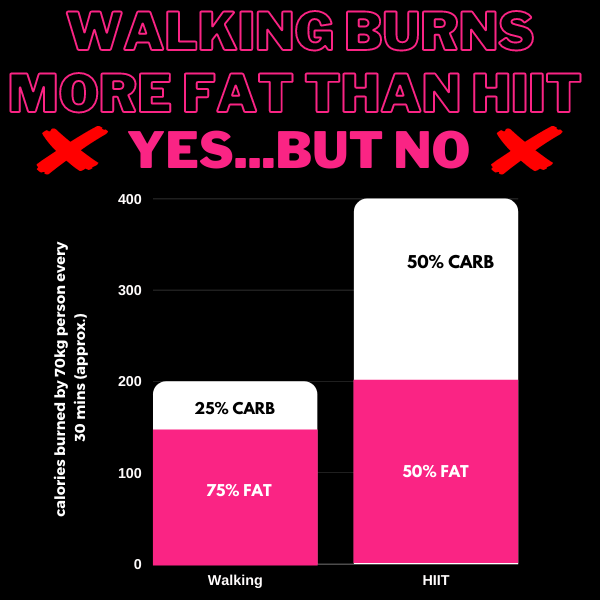
You will hear all too often that if you are trying to lose body fat, you should walk rather than run because you burn more fat by walking. This is partly true but these people have just misunderstood the data.
When you walk at a low intensity, around 75% of the calories you use will come from body fat. During a HIIT session only 50% (or less) of the calories burned will come from body fat.
This is where the ‘low intensity’ advocators have closed the book. What has been completely missed is that, while HIIT burns a lower PROPORTION of fat, it will burn a greater AMOUNT of fat (as demonstrated by the table).
To put the icing on the cake, when your glycogen (carbohydrate) stores get low (due to higher intensity exercise), the carbohydrates from the food you eat will later get converted into glycogen to top up the depleted stores, and therefore, will not be converted to body fat when they are left unused for energy.
As we mention all the time, HIIT will also boost your metabolism after you have completed your workout. What this means, is that your body will continue to burn calories hours after you have finished your workout. This is because during recovery from this type of exercise, energy (calories) is needed to return your body to a resting state and adapt it to the exercise just performed. This process is known as EPOC (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption). Once a state of EPOC is achieved, your body will continue to burn more calories after your session as it tries to recover from the activity just performed. This includes hormone balancing, removal of waste products, replenishment of fuel stores, cellular repair, fueling the body’s increase in metabolism due to the increase in body temperature and many more bodily processes. This means that you have the potential to keep burning calories for up to 36 hours after your workout! This effect is nearly non-existent in low intensity exercise.